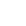
Popular plant-based nutritional health ingredients: Ivy extract
Author : Naturalin Date : Click : times
In the booming field of plant-based nutrition, more and more natural ingredients are gaining attention for their potential health benefits. Among them, ivy extract, derived from the leaves of the evergreen climbing plant Hedera helix, has become a popular ingredient in the health, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. With potential effects from relieving respiratory discomfort to nourishing the skin, this ancient medicinal extract is favored by modern consumers for its diverse nutritional value. Let’s dive deep into the world of ivy extract and explore its properties.

Ivy extract is a natural compound extracted from the leaves of English ivy (Hedera helix) or Chinese ivy (Hedera nepalensis var. sinensis), with a typical appearance of light yellow fine powder. It should be emphasized that fresh ivy leaves are toxic and cannot be consumed directly; the commercially available extract is produced through standardized extraction processes under strict quality control to ensure relative safety and stability.
The potential health benefits of ivy extract are associated with its rich and diverse active components, mainly including:
1.Triterpenoid saponins: The core active ingredients, such as hederacoside C, alpha-hederin, and hederagenin. Studies have shown that alpha-hederin has expectorant potential, which may help loosen phlegm and mucus in the respiratory tract, while hederacoside C and hederagenin have shown anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potential in relevant studies.
2.Flavonoids: As natural plant pigments, flavonoids in ivy extract have shown antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential in studies, which may help scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the body.
3.Phenolic acids and polyphenols: These compounds may enhance the antioxidant capacity of ivy extract, which is conducive to protecting cells from damage caused by environmental factors and metabolic processes, and may have a positive effect on reducing the risk of chronic diseases (note: this does not mean having the function of preventing or treating chronic diseases).
1. Potential Effect on Respiratory Health: Relieving Cough and Unblocking Airways
One of the widely studied aspects of ivy extract is its potential effect on respiratory health. Relevant studies have shown that it may have expectorant and bronchodilator potential: the saponin components may thin thick mucus in the airways, making it easier to cough up and clear the lungs, and may also relax the bronchial muscles to widen the airways and improve breathing comfort (note: this does not mean having the function of treating respiratory diseases).
A number of clinical studies have explored its potential in relieving respiratory symptoms. Relevant meta-analyses have shown that patients with acute respiratory tract infections who took ivy leaf dry extract for 7 days had a tendency of reduced cough frequency and severity compared to the placebo group, and the proportion of cough-free patients was relatively higher during follow-up. It should be emphasized that this does not mean that ivy extract can treat chronic respiratory conditions such as bronchitis, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); it can only be used as an auxiliary conditioning component under professional guidance.
2. Potential Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects: Relevant Research Directions
Inflammation and oxidative stress are associated with the occurrence and development of many chronic diseases, including arthritis, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. Studies have shown that the bioactive compounds in ivy extract, such as saponins and flavonoids, may exert potential anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators like cytokines (e.g., IL-6) and prostaglandins. It should be emphasized that this does not mean having the function of treating diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis; it is only a research direction of potential auxiliary effects.
Meanwhile, its rich antioxidants (flavonoids, phenolic acids, etc.) may scavenge free radicals in the body, neutralize their harmful effects, and enhance the body’s antioxidant defense system. It should be noted that this does not mean having the function of preventing or treating chronic diseases induced by oxidative stress.
3. Potential Skin Nourishing Effects: Application in Cosmetics
Ivy extract has become a popular ingredient in the cosmetic industry due to its potential skin-nourishing properties. Its antioxidant components may help reduce the damage of free radicals to the skin, slow down the skin aging process, and help maintain skin elasticity. Additionally, relevant studies have shown that it may have the potential to promote collagen production (a key protein for skin firmness), and is widely used as an auxiliary component in anti-aging skincare products (note: it does not have the effect of "removing wrinkles" or "anti-aging" as a therapeutic effect).
For acne-prone skin, the potential anti-inflammatory properties of ivy extract may help alleviate skin redness and swelling. Its ability to unclog pores and inhibit sebum production may help improve skin conditions prone to acne, making it suitable for oil-control and acne-improving skincare products. It also has a moisturizing effect, which can hydrate dry skin and help improve skin texture.
4. Other Potential Research Directions
Recent studies have explored the potential of ivy extract in aiding weight management by boosting metabolism and suppressing appetite, but this is still in the research stage and has not been confirmed as a definite effect. Its tannin components may help improve mild diarrhea symptoms, and it also has potential antimicrobial activity, which may inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria (e.g., Salmonella and E. coli) and fungi, and is a potential natural preservative component.
Thanks to its diverse benefits, ivy extract has been widely applied in multiple fields:
1.Pharmaceuticals and health products: It is made into capsules, tablets, syrups, tinctures, and oral liquids, which are used as auxiliary components for relieving cough symptoms, improving respiratory comfort, and regulating body functions. Common cough syrups containing ivy extract (such as Prospan) are widely available over-the-counter, and should be used in accordance with the instructions or under the guidance of professionals. It should be emphasized that health products containing ivy extract cannot replace drugs.
2.Cosmetics: Used in anti-aging creams, sunscreens, acne products, moisturizers, shampoos, and anti-cellulite creams, catering to various skin care needs.
3.Food and beverages: As a natural nutritional fortifier, it is added to drinks, dairy products, and baked goods to help enhance product nutritional value and extend shelf life through its antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.
Conclusion
About Naturalin
References
1. Cathers, M. (2024). Ivy leaf for cough relief. American Pharmacists Association Blog.
2. WebMD. (2025). English Ivy - Uses, Side Effects, and More.
3. Cinski, E. S., Holzinger, F., & Chenot, J.-F. (2021). Ivy leaf (Hedera helix) for acute upper respiratory tract infections: an updated systematic review. PubMed Central.
4. Green Sky Bio. (2024). 10 Amazing Health Benefits of Ivy Extract.
5. Nanjing NutriHerb BioTech Co.,Ltd. (2025). Ivy leaf Extract.
- Next Page:How do plant extracts promote eye health?
-
 Return list
Return list
- Previous Page:The Function and Application of Astragalus Extract
 sales@naturalin.com
sales@naturalin.com +86(731)84430651
+86(731)84430651