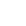
How Ginkgo Biloba Extract Promotes Immune Health
Author : Naturalin Date : Click : times
Key Bioactive Components of Ginkgo Biloba Extract
Mechanisms of Action in Boosting Immune Health
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are inevitable byproducts of cellular metabolism, and excessive ROS accumulation can cause oxidative stress, impairing the function and viability of immune cells such as macrophages, T cells, and B cells. Ginkgo Biloba Extract’s flavonoids and terpenoids act as powerful antioxidants, scavenging free radicals and neutralizing ROS. By reducing oxidative damage to immune cells, these compounds help maintain the integrity and functionality of the immune system, ensuring that immune cells can efficiently recognize and eliminate pathogens. For example, quercetin, a major flavonoid in Ginkgo Biloba Extract, has been shown to upregulate the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) in immune cells, further enhancing their resistance to oxidative stress.
Modulation of Immune Cell Activity
Ginkgo Biloba Extract exerts a dual regulatory effect on immune cell function, balancing both innate and adaptive immune responses. In the innate immune system, it enhances the phagocytic activity of macrophages, enabling these cells to more effectively engulf and destroy bacteria, viruses, and other foreign particles. Studies have demonstrated that Ginkgo Biloba Extract stimulates the production of immune-modulating cytokines by macrophages, including interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which play crucial roles in initiating and amplifying immune responses.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects to Reduce Immune Burden
Chronic inflammation can disrupt immune homeostasis, leading to immune dysfunction and an increased risk of chronic diseases. Ginkgo Biloba Extract exhibits significant anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. It suppresses the activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), a key signaling pathway involved in regulating inflammatory responses, thereby reducing the release of pro-inflammatory molecules such as IL-6, TNF-α, and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). By alleviating chronic inflammation, Ginkgo Biloba Extract reduces the immune system’s burden, allowing it to focus on defending against external threats rather than combating persistent internal inflammation. This anti-inflammatory effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with inflammatory conditions that compromise immune function.
Applications in Health and Wellness
Ginkgo Biloba Extract is widely used in dietary supplements, either as a single-ingredient product or as part of synergistic blends with other immune-supporting ingredients. For example, supplements combining Ginkgo Biloba Extract with Vitamin C, Zinc, or Echinacea Extract offer comprehensive immune support, targeting multiple aspects of immune function. These supplements are popular among individuals seeking natural ways to enhance their immune system, including the elderly, athletes, and those under chronic stress. Meanwhile, other recommended plant extracts are also extensively incorporated into dietary supplements—Chaga Mushroom Extract and Ginseng Extract blends provide comprehensive immune support, while Echinacea and Ivy Extract combinations focus on respiratory health, ideal for seasonal cold prevention or managing chronic respiratory conditions.
Functional Foods and Beverages
The incorporation of Ginkgo Biloba Extract into functional foods and beverages has become increasingly common, providing consumers with convenient ways to integrate immune-supporting ingredients into their daily diets. Ginkgo Biloba-infused teas, smoothies, and energy drinks are readily available in the market, catering to health-conscious consumers who prefer natural and accessible immune-boosting options. Similarly, other plant extracts are added to functional foods and beverages to amplify immune benefits—Echinacea-infused teas, Chaga coffee blends, and ginseng-fortified smoothies allow consumers to easily incorporate immune-supporting ingredients into their daily lives.
Potential Pharmaceutical Applications
While Ginkgo Biloba Extract is primarily used in nutraceuticals and functional foods, ongoing research is exploring its potential in pharmaceutical formulations. Preliminary studies suggest that Ginkgo Biloba Extract may have adjuvant effects in vaccines, enhancing the body’s immune response to vaccine antigens. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating properties make it a promising candidate for the development of drugs targeting immune-related disorders, such as autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiencies. For other plant extracts, Ivy Extract is often utilized in cough syrups and respiratory medications to alleviate symptoms of chronic bronchitis and asthma, and Echinacea Extract is found in over-the-counter supplements for URTI relief, backed by clinical evidence of its efficacy. Further clinical trials are needed to validate the full potential of these plant extracts in pharmaceutical applications.
Conclusion
References
1. Kim, S., Lee, J., & Park, H. (2023). Immunomodulatory effects of Chaga mushroom (Inonotus obliquus) polysaccharides in human PBMCs. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 312, 116345.
2. Cochrane Collaboration. (2024). Echinacea for preventing and treating upper respiratory tract infections. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 5, CD000530.
3. Lee, H., Kim, Y., & Kim, J. (2022). Ginsenoside Rg1 improves immune function in aged mice via regulating T cell subsets and cytokine production. Journal of Medicinal Food, 25(8), 821 - 828.
4. Müller, J., & Hansel, R. (2021). Efficacy and safety of ivy extract (Hedera helix) in patients with chronic bronchitis: A randomized controlled trial. Phytomedicine, 83, 153689.
5. Wasser, S. P. (2022). Medicinal mushrooms as a source of immunomodulating polysaccharides. International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms, 24(1), 1 - 25.
 sales@naturalin.com
sales@naturalin.com +86(731)84430651
+86(731)84430651









 Return list
Return list